Backbone cabling in an enterprise – In the heart of every enterprise, the backbone cabling system serves as the vital infrastructure that connects devices, facilitates communication, and ensures seamless data flow. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of backbone cabling, empowering you to design, install, maintain, and troubleshoot this critical component of your network infrastructure.
As the backbone of your enterprise network, this cabling system plays a pivotal role in supporting business operations, enhancing productivity, and safeguarding data integrity. By understanding the principles and best practices Artikeld in this guide, you can harness the full potential of backbone cabling and drive your enterprise towards digital excellence.
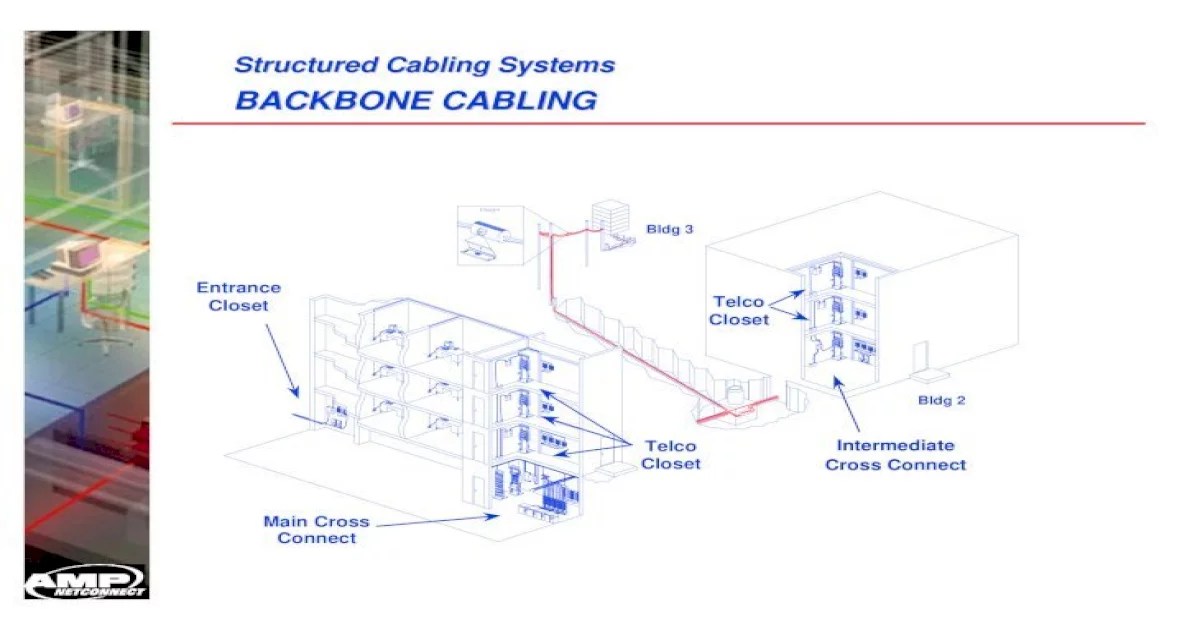
Backbone Cabling Infrastructure Overview
Backbone cabling is the foundation of an enterprise network, providing the high-speed connectivity that supports critical business applications and services. It interconnects key network devices, such as routers, switches, and servers, forming the backbone of the network’s infrastructure.
Types of Backbone Cabling
Backbone cabling can be implemented using various types of cables, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Fiber Optic Cabling:Fiber optic cables transmit data using light pulses, offering extremely high bandwidth and low signal loss over long distances, making them ideal for high-speed applications.
- Copper Cabling:Copper cables transmit data using electrical signals, providing a cost-effective and reliable solution for shorter distances and lower bandwidth requirements.
Hierarchical Structure of Backbone Cabling
Backbone cabling is typically organized in a hierarchical structure, with multiple layers of cabling connecting different network devices:
- Core Layer:The core layer forms the central backbone of the network, connecting major network devices and providing high-speed connectivity across the enterprise.
- Distribution Layer:The distribution layer distributes traffic from the core layer to smaller network segments, such as workgroups or departments.
- Access Layer:The access layer connects individual devices, such as workstations, servers, and printers, to the network.
Backbone Cabling Design and Planning
Designing and planning a robust backbone cabling system is crucial for supporting the network’s infrastructure. This involves determining the network topology, estimating capacity requirements, and considering future scalability to ensure the system meets current and anticipated demands.
Proper documentation and labeling are essential for effective cable management. This enables efficient troubleshooting, upgrades, and maintenance, minimizing downtime and ensuring the smooth operation of the network.
Network Topology
- Define the physical layout and connectivity of network devices, including routers, switches, and servers.
- Choose a topology that aligns with the network’s requirements, such as star, bus, ring, or mesh.
Capacity Requirements
- Estimate the current and future bandwidth needs based on network traffic patterns and applications.
- Consider factors such as the number of users, network utilization, and anticipated growth.
Future Scalability
- Design the cabling system with the potential for future expansion and upgrades in mind.
- Use modular components and standardized cabling practices to facilitate changes and additions.
Documentation and Labeling
Maintain accurate records of the cabling system, including cable types, lengths, and connections.
Label cables clearly and consistently to simplify identification and troubleshooting.
Backbone Cabling Installation and Maintenance
Backbone cabling installation and maintenance are critical aspects of ensuring a reliable and high-performing network infrastructure. Proper installation techniques and ongoing maintenance procedures are essential for optimal network performance and longevity.
During installation, careful attention should be paid to cable routing, termination, and testing to ensure signal integrity and prevent potential issues.
Tools and Equipment for Professional Installation, Backbone cabling in an enterprise
Professional installation requires specialized tools and equipment, including:
- Cable strippers for removing the outer jacket and exposing the conductors
- Punch-down tools for terminating cables into patch panels and wall outlets
- Cable testers for verifying cable continuity and performance
- Label makers for identifying cables and patch panels
- Cable ties and Velcro straps for securing and organizing cables
Ongoing Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of backbone cabling. Maintenance procedures include:
- Visual inspections for any physical damage or wear
- Cable testing to identify any potential faults or degradation
- Cleaning and dusting to prevent dust and debris accumulation
- Documentation and labeling for easy identification and troubleshooting
- Regular software updates for network management systems
Backbone Cabling Standards and Regulations
Backbone cabling installations are governed by a comprehensive set of industry standards and regulations to ensure reliability, performance, and safety. These standards provide guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of backbone cabling infrastructure, ensuring adherence to best practices and compliance with relevant codes.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is crucial for several reasons. It ensures that:
- Safety:Adhering to safety regulations minimizes the risk of electrical hazards, fires, and other accidents.
- Performance:Following design and installation standards optimizes network performance, ensuring reliable data transmission and minimizing downtime.
- Interoperability:Compliance with standards enables seamless integration of different network components, ensuring compatibility and efficient communication.
- Legal Liability:Non-compliance with regulations can lead to legal liability and penalties, including fines or sanctions.
Role of Certification and Accreditation
Certification and accreditation play a vital role in ensuring quality backbone cabling installations. Certification programs validate the skills and knowledge of cabling professionals, while accreditation programs recognize companies that meet specific quality standards.
Certified cabling professionals have demonstrated proficiency in the design, installation, and maintenance of backbone cabling systems. They are equipped with the expertise to ensure that installations meet industry standards and regulations, maximizing performance and reliability.
Accredited companies have undergone rigorous audits to demonstrate their commitment to quality and adherence to best practices. They employ certified professionals, utilize high-quality materials, and follow standardized processes to deliver exceptional cabling installations.
Backbone Cabling Security Considerations
Securing backbone cabling is paramount to safeguard data and maintain network integrity. Unauthorized access and data breaches pose significant risks that demand effective security measures.
Physical security measures protect cables from tampering and unauthorized access. Cable trays and locked cabinets provide a secure physical environment for cables, preventing unauthorized personnel from accessing or manipulating them.
Network Security Measures
Network security measures enhance the protection of data transmitted over backbone cabling.
- Encryptionsafeguards data by converting it into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access and eavesdropping.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, detecting and alerting administrators to potential security breaches.
Backbone Cabling Troubleshooting and Repair
Troubleshooting and repairing backbone cabling issues is essential for maintaining network uptime and ensuring efficient data transmission. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to identifying, diagnosing, and resolving common problems associated with backbone cabling infrastructure.
Diagnostic Techniques and Tools
Effective troubleshooting requires a systematic approach using appropriate diagnostic tools. These include:
Cable testers
Verify cable continuity, length, and wire map.
Time-domain reflectometers (TDRs)
Detect cable faults and measure cable length.
Optical time-domain reflectometers (OTDRs)
Test fiber optic cables for faults, attenuation, and splice loss.
Backbone Cabling Case Studies and Examples
Backbone cabling plays a critical role in the performance and reliability of enterprise networks. Here are some case studies and examples that demonstrate the benefits of a well-designed and maintained backbone cabling system:
Case Study: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a global financial services firm, implemented a new backbone cabling system to support its growing data center operations. The company used a hierarchical design with multiple layers of redundancy to ensure high availability and performance. The new system reduced network downtime by 90% and improved application response times by 30%. The company also realized significant cost savings by consolidating its data centers and reducing its power consumption.
Best Practice: Data Center Interconnect
Data centers often require high-speed and reliable connectivity between multiple buildings or campuses. One best practice for data center interconnect is to use fiber optic cables with multiple strands to provide redundant paths and increase bandwidth capacity. This approach ensures that data can be transmitted quickly and securely between data centers, even in the event of a cable failure.
Innovative Design: Campus-Wide Network
Universities and corporate campuses often have a large number of buildings that need to be connected to a central network. One innovative design for campus-wide networks is to use a distributed backbone architecture. This approach uses multiple backbone switches located throughout the campus, which are connected to each other with high-speed fiber optic cables.
This design provides greater flexibility and scalability, as new buildings or departments can be easily added to the network without disrupting existing services.
FAQ Resource: Backbone Cabling In An Enterprise
What are the key considerations for designing a backbone cabling system?
Factors to consider include network topology, capacity requirements, future scalability, and ease of maintenance.
What are the best practices for installing backbone cabling?
Proper cable routing, termination, and testing are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
What are the common security concerns related to backbone cabling?
Unauthorized access, data breaches, and physical damage are potential security risks that need to be addressed.
What are the benefits of a well-designed and maintained backbone cabling system?
Improved network performance, enhanced reliability, increased scalability, and reduced downtime are some of the key benefits.