Embark on a journey through the electromagnetic spectrum worksheet answer key, a gateway to understanding the fundamental nature of light and its diverse applications. This comprehensive resource unveils the intricacies of the spectrum, guiding you through its various regions, properties, and real-world applications.
From the high-energy gamma rays to the ubiquitous radio waves, the electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of frequencies and wavelengths, each with unique characteristics and practical implications. Delve into the properties of each region, exploring their applications in medicine, communication, and countless other fields.
Electromagnetic Spectrum Overview
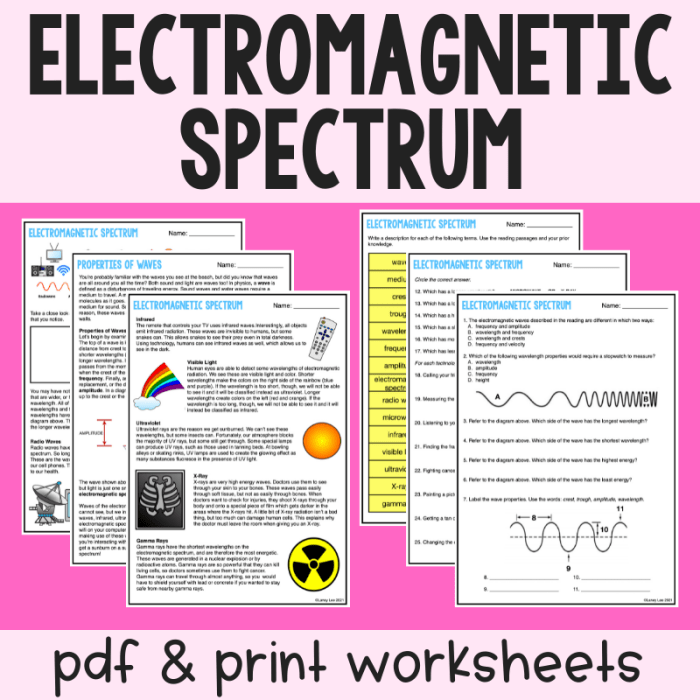
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. It includes all types of electromagnetic radiation, from gamma rays to radio waves. The electromagnetic spectrum is often divided into seven regions, each with its own unique properties and characteristics.
The electromagnetic spectrum is a useful tool for understanding the universe. It can be used to study the stars, planets, and galaxies. It can also be used to develop new technologies, such as lasers and MRI machines.
Regions of the Electromagnetic Spectrum, The electromagnetic spectrum worksheet answer key
- Gamma rayshave the shortest wavelengths and the highest frequencies. They are produced by radioactive decay and other high-energy processes.
- X-rayshave shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet radiation and longer wavelengths than gamma rays. They are produced by the bombardment of high-energy electrons on matter.
- Ultraviolet radiationhas shorter wavelengths than visible light and longer wavelengths than X-rays. It is produced by the sun and other hot objects.
- Visible lighthas wavelengths that can be seen by the human eye. It is produced by the sun and other light sources.
- Infrared radiationhas longer wavelengths than visible light and shorter wavelengths than microwaves. It is produced by warm objects.
- Microwaveshave longer wavelengths than infrared radiation and shorter wavelengths than radio waves. They are produced by electronic devices and other sources.
- Radio waveshave the longest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies. They are produced by electrical currents and other sources.
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy that is emitted by charged particles. It consists of electric and magnetic fields that oscillate in phase, perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation.
Electromagnetic radiation is produced when charged particles are accelerated. This can happen when particles are heated, when they are subjected to a magnetic field, or when they are exposed to other forms of electromagnetic radiation.
Electromagnetic radiation can be classified according to its wavelength or frequency. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency. The different types of electromagnetic radiation are:
- Gamma rays
- X-rays
- Ultraviolet radiation
- Visible light
- Infrared radiation
- Microwaves
- Radio waves
Applications of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum has a wide range of applications in science, medicine, and industry.
Science
- Astronomy: Astronomers use electromagnetic radiation to study the stars, planets, and galaxies.
- Medicine: Doctors use electromagnetic radiation to diagnose and treat diseases.
- Industry: Engineers use electromagnetic radiation to develop new technologies, such as lasers and MRI machines.
Medicine
- X-raysare used to diagnose broken bones and other injuries.
- Ultraviolet radiationis used to treat skin conditions such as psoriasis.
- Microwavesare used to heat food and cook meals.
Industry
- Lasersare used to cut metal and other materials.
- MRI machinesare used to create images of the inside of the body.
- Radio wavesare used to transmit information over long distances.
Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answer Key
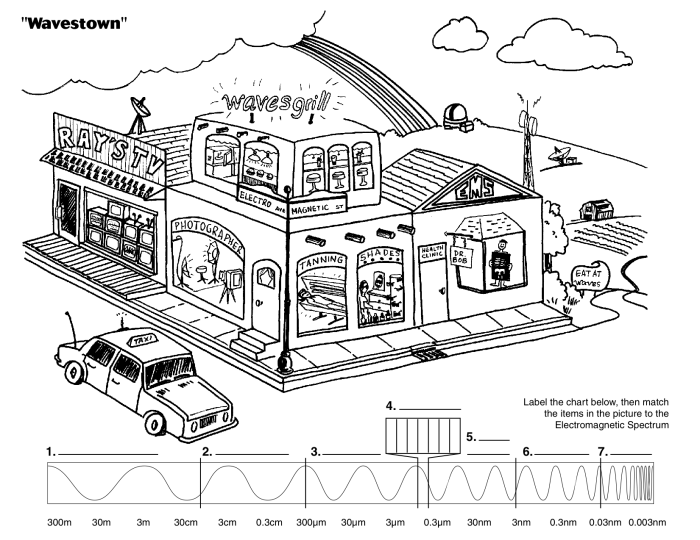
| Region of the Spectrum | Wavelength Range | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma rays | <10^-12 m | High energy, ionizing | Cancer treatment, sterilization |
| X-rays | 10^-12
|
High energy, ionizing | Medical imaging, security screening |
| Ultraviolet radiation | 10^-8
|
High energy, non-ionizing | Sun tanning, water purification |
| Visible light | 400
|
Visible to the human eye | Photography, lighting |
| Infrared radiation | 700 nm
|
Low energy, non-ionizing | Night vision, heat detection |
| Microwaves | 1 mm
|
Low energy, non-ionizing | Microwave ovens, radar |
| Radio waves | >30 cm | Very low energy, non-ionizing | Radio communication, television |
Clarifying Questions: The Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answer Key
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, visible light, infrared radiation, microwaves, and radio waves.
What are the properties of each region of the electromagnetic spectrum?
Each region of the electromagnetic spectrum has unique properties, such as wavelength, frequency, energy, and ability to penetrate matter.
What are the applications of the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum has a wide range of applications in fields such as medicine, communication, industry, and scientific research.


