Embark on an enthralling journey through the APUSH French and Indian War, a pivotal conflict that reshaped the destiny of North America. This war, a clash of empires and cultures, left an indelible mark on the American colonies and Native American tribes, setting the stage for the birth of a new nation.
From the spark of European rivalries to the alliances and strategies that fueled the flames, we delve into the intricacies of this complex conflict, exploring its causes, major battles, and far-reaching consequences.
Overview of the French and Indian War: Apush French And Indian War
The French and Indian War, also known as the Seven Years’ War, was a global conflict that lasted from 1754 to 1763. It pitted the British Empire against the French Empire, with their respective Native American allies, over control of North America.
The war began with a series of skirmishes in the Ohio River Valley, where British and French traders competed for control of the fur trade. As tensions escalated, both sides began to build alliances with Native American tribes, who played a significant role in the conflict.
Major Battles and Events
The war was marked by several major battles, including:
- The Battle of Fort Duquesne (1755): A British defeat that led to the capture of General Edward Braddock.
- The Battle of Fort William Henry (1757): A French victory that resulted in the massacre of British prisoners.
- The Battle of Quebec (1759): A decisive British victory that led to the capture of Quebec City and the death of French General Louis-Joseph de Montcalm.
The war also saw the rise of George Washington, who served as a young officer in the Virginia militia.
Impact on the American Colonies and Native American Tribes
The French and Indian War had a profound impact on the American colonies and Native American tribes.
- For the colonies, the war led to increased British control over their affairs. The British Parliament passed a series of laws, such as the Stamp Act and the Townshend Acts, which imposed new taxes and restrictions on the colonies.
- For Native American tribes, the war resulted in a loss of land and power. The British victory at the Battle of Quebec marked the beginning of a period of decline for Native American influence in the Ohio River Valley and the Great Lakes region.
European Rivalries in North America
The French and Indian War was a major conflict between European powers in North America that took place from 1754 to 1763. The war was fought between Great Britain and France, with their respective Native American allies.The main motivations for the war were the competing claims of Great Britain and France to land in North America.
Great Britain wanted to expand its colonies westward, while France wanted to protect its existing colonies and expand its own territory.Both Great Britain and France used alliances with Native American tribes to their advantage. The British allied with the Iroquois Confederacy, while the French allied with the Algonquian tribes.
These alliances played a significant role in the war, as they provided both sides with valuable military support.In addition to alliances, diplomacy also played a role in the war. Both Great Britain and France attempted to negotiate treaties with each other, but these negotiations were unsuccessful.
The war eventually ended with the Treaty of Paris in 1763, which gave Great Britain control of all French territory in North America east of the Mississippi River.
Competing European Powers
The main European powers involved in the French and Indian War were Great Britain and France.Great Britain* Motivations: Expand its colonies westward, protect its existing colonies, and gain control of the fur trade.
Strategies
Allied with the Iroquois Confederacy, built forts in the Ohio Valley, and sent troops to North America.France* Motivations: Protect its existing colonies, expand its territory, and gain control of the fur trade.
Strategies
Allied with the Algonquian tribes, built forts in the Ohio Valley, and sent troops to North America.
Alliances and Diplomacy
Alliances and diplomacy played a significant role in the French and Indian War.Alliances* Both Great Britain and France allied with Native American tribes.
- The British allied with the Iroquois Confederacy, while the French allied with the Algonquian tribes.
- These alliances provided both sides with valuable military support.
Diplomacy* Both Great Britain and France attempted to negotiate treaties with each other.
- These negotiations were unsuccessful.
- The war eventually ended with the Treaty of Paris in 1763, which gave Great Britain control of all French territory in North America east of the Mississippi River.
The Role of Native American Tribes

Native American tribes played a significant role in the French and Indian War, allying with both the French and British. Their motivations were complex, including a desire to protect their lands, maintain their traditional way of life, and gain access to European goods.
The APUSH French and Indian War, a pivotal conflict in American history, serves as a poignant example of the complex question: “Is our gain also our loss?” The war, sparked by competing territorial claims, led to significant gains for Britain and its colonies.
Yet, these gains came at a cost. The war strained relations with Native American tribes, fueling resentment that would culminate in further conflicts. As we explore the legacies of the APUSH French and Indian War, it is imperative to consider the enduring relevance of this timeless question: is our gain also our loss .
Alliances and Motivations
The Iroquois Confederacy, a powerful alliance of six tribes in the Northeast, initially allied with the British. They were motivated by a desire to protect their lands from French encroachment and to maintain their dominance over other Native American tribes.
The Shawnee, Delaware, and Lenape tribes in the Ohio Valley allied with the French. They were motivated by a desire to resist British expansion into their territories and to gain access to French goods, such as guns and ammunition.
Impact on Native American Societies
The French and Indian War had a devastating impact on Native American societies. The war led to the loss of many lives, the disruption of traditional economies, and the displacement of tribes from their ancestral lands. The war also exacerbated tensions between Native American tribes and European settlers, leading to increased conflict and violence in the years to come.
The Albany Congress and Colonial Unity

The Albany Congress, convened in 1754, aimed to foster unity among the British colonies in North America during the French and Indian War. The Congress was organized by the British government in an effort to establish a unified colonial front against the French threat.The
Congress faced numerous challenges in its quest for colonial unity. Colonial delegates held diverse interests and perspectives, making it difficult to reach a consensus on a common strategy. Additionally, the colonies had a history of distrust and rivalry, further hindering the development of a cohesive alliance.Despite
these obstacles, the Albany Congress managed to achieve some important outcomes. The Congress produced the Albany Plan of Union, a proposal for a unified colonial government that would coordinate defense and other matters. Although the plan was ultimately rejected by the colonial assemblies, it laid the groundwork for future discussions about colonial cooperation.The
Albany Congress also helped to establish a sense of common purpose among the colonies. By bringing together representatives from different regions, the Congress fostered a greater understanding of the shared challenges facing the colonies. This sense of unity would later prove invaluable during the American Revolution.
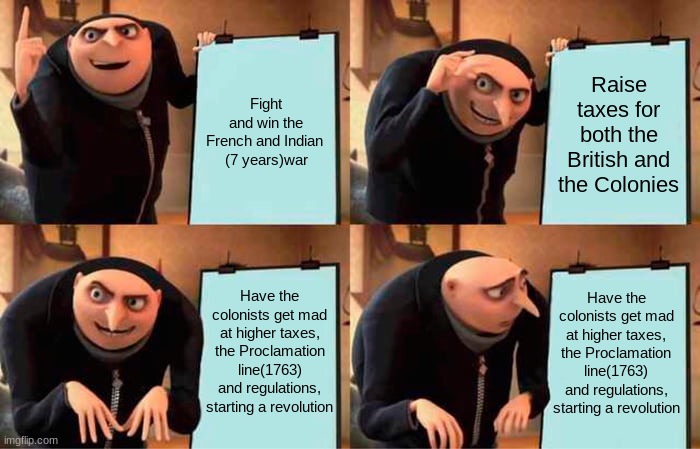
The Impact of the War on British Colonial Policy

The French and Indian War had a profound impact on British colonial policy towards the American colonies. The war revealed the weaknesses of the existing system of colonial administration and led to a shift in British policy towards a more centralized and assertive approach.
Increased Imperial Control, Apush french and indian war
One of the most significant changes in British policy was the increased level of imperial control over the colonies. The war had shown that the colonies were not capable of defending themselves without British assistance, and this led to a greater willingness on the part of the British government to intervene in colonial affairs.
- The Proclamation of 1763 forbade settlement west of the Appalachian Mountains, a measure designed to prevent conflict with Native American tribes and to maintain control over the fur trade.
- The Currency Act of 1764 prohibited the colonies from issuing their own paper money, a move intended to stabilize the colonial economy and prevent inflation.
- The Stamp Act of 1765 imposed a tax on all printed materials in the colonies, sparking widespread protests and leading to the formation of the Stamp Act Congress.
These measures were met with resistance from the colonies, who argued that they violated their rights as British subjects. However, the British government was determined to assert its authority, and the result was a series of conflicts that culminated in the American Revolution.
Common Queries
What were the primary causes of the APUSH French and Indian War?
Competing claims over land and resources between France and Great Britain, as well as the desire for control of the Ohio River Valley.
How did Native American tribes participate in the war?
They formed alliances with both French and British forces, seeking to protect their territories and influence the outcome of the conflict.
What was the significance of the Albany Congress?
It was an attempt to unify the American colonies against the French threat, but it ultimately failed due to disagreements over representation and authority.