National electrical code table 310-16 – National Electrical Code (NEC) Table 310-16 stands as a cornerstone of electrical design, providing essential guidelines for the proper sizing and installation of electrical conductors. This comprehensive resource ensures the safety and efficiency of electrical systems, empowering professionals to navigate the complexities of electrical wiring with confidence.
NEC Table 310-16 encompasses a wide range of topics, including ampacity ratings, conductor types, installation methods, and real-world applications. By delving into these aspects, we gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence conductor performance and the critical role they play in ensuring electrical system integrity.
1. Understanding National Electrical Code (NEC) Table 310-16
NEC Table 310-16 provides essential information for selecting the correct size and type of electrical conductors for various applications. It is a critical resource for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Purpose and Scope
The purpose of NEC Table 310-16 is to specify the ampacity ratings of electrical conductors based on their physical characteristics and installation conditions. It applies to all electrical conductors used in buildings, including residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Conductor Types Covered
NEC Table 310-16 covers a wide range of electrical conductors, including:
- Copper conductors
- Aluminum conductors
- Steel conductors
- Conductors with insulation materials such as PVC, XLPE, and THHN
Applications
NEC Table 310-16 is used in various electrical design applications, such as:
- Sizing electrical conductors for branch circuits
- Determining the ampacity of feeders and service entrance conductors
- Selecting the appropriate conductor for motor circuits
2. Ampacity Ratings and Adjustments
Ampacity
Ampacity refers to the maximum current that a conductor can safely carry without exceeding its temperature rating. It is determined by factors such as the conductor material, size, insulation, and ambient temperature.
Factors Affecting Ampacity
The following factors affect the ampacity of electrical conductors:
- Conductor material (e.g., copper, aluminum)
- Conductor size (e.g., AWG gauge)
- Insulation type (e.g., PVC, XLPE)
- Ambient temperature
- Number of conductors in a raceway
Adjusting Ampacity Ratings
NEC Table 310-16 provides adjustment factors to modify the ampacity ratings of conductors based on installation conditions. These factors include:
- Temperature correction factors
- Raceway adjustment factors
- Conductors in parallel
3. Conductor Types and Properties: National Electrical Code Table 310-16
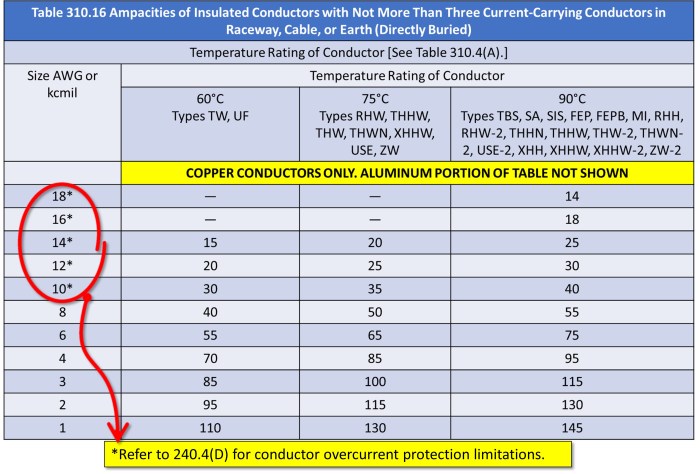
Types of Conductors, National electrical code table 310-16
The most common types of electrical conductors used in wiring are:
- Copper conductors: Excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and ductility
- Aluminum conductors: Lighter than copper, but higher resistance
- Steel conductors: High strength, but lower conductivity than copper and aluminum
Conductor Properties
Important properties of electrical conductors include:
- Conductivity: Ability to conduct electricity
- Resistance: Opposition to the flow of electricity
- Ampacity: Maximum current-carrying capacity
- Tensile strength: Ability to withstand pulling forces
4. Conductor Sizing and Selection
Selecting Conductor Size
The correct conductor size is essential for ensuring safe and reliable electrical operation. The following steps should be followed when selecting the conductor size:
- Determine the load current
- Select the appropriate conductor type
- Use NEC Table 310-16 to determine the minimum ampacity
- Apply any necessary adjustment factors
- Select the conductor size that meets or exceeds the calculated ampacity
- Load current
- Voltage drop
- Environmental conditions
- Code requirements
- Conduit
- Cable trays
- Open wiring
- Underground burial
- Proper grounding
- Avoiding overcurrent conditions
- Protecting conductors from physical damage
- Following NEC requirements
- Residential wiring
- Commercial building wiring
- Industrial plant wiring
- Motor circuits
- Oversized conductors preventing overheating and electrical fires
- Properly installed conductors reducing voltage drop and ensuring efficient operation
- Underground burial protecting conductors from environmental hazards
Factors to Consider
Factors to consider when selecting a conductor size include:
5. Installation Methods and Requirements
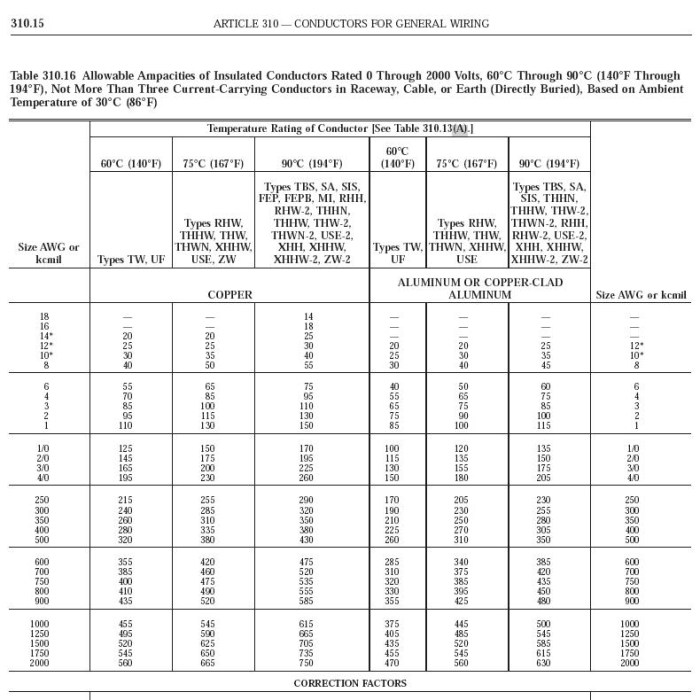
Installation Methods
Electrical conductors can be installed using various methods, including:
NEC Requirements
NEC specifies requirements for conductor spacing, support, and protection. These requirements ensure the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems.
Safety Considerations
Important safety considerations for conductor installation include:
6. Applications and Case Studies
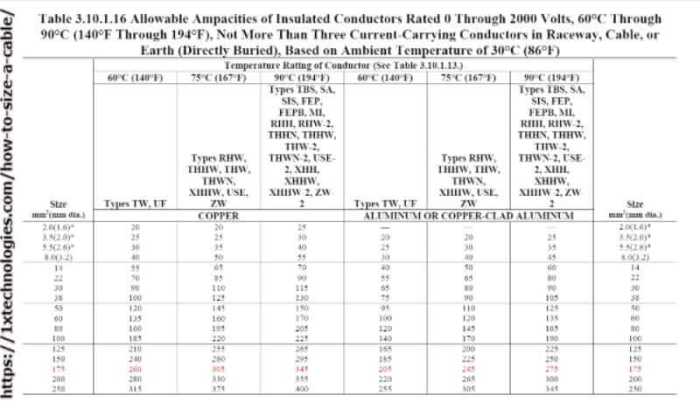
Applications
NEC Table 310-16 is applied in various electrical design applications, such as:
Case Studies
Case studies demonstrate the importance of proper conductor sizing and installation. Examples include:
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of NEC Table 310-16?
NEC Table 310-16 provides guidelines for the selection and installation of electrical conductors, ensuring their safe and efficient operation.
What factors affect the ampacity rating of a conductor?
Conductor type, temperature, and insulation are key factors that influence ampacity ratings.
How do I select the appropriate conductor size for a given application?
NEC Table 310-16 provides a step-by-step process for conductor sizing, considering load current, voltage drop, and environmental conditions.
What are the common types of electrical conductors?
Copper, aluminum, and steel are widely used conductor materials, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
What are the safety considerations for conductor installation?
Proper spacing, support, and protection are crucial for safe conductor installation, minimizing the risk of electrical hazards.