What is the main risk factor for wandering and elopement? This question is of paramount importance in the field of geriatric care, as wandering and elopement pose significant risks to the safety and well-being of elderly individuals. In this article, we will delve into the various factors that contribute to wandering and elopement, with a particular focus on identifying the most significant risk factor.
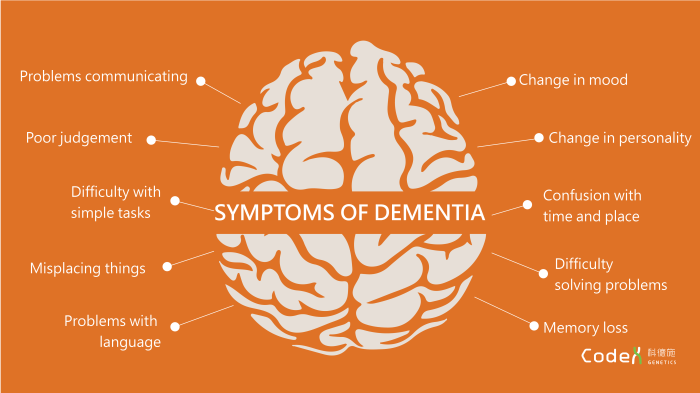
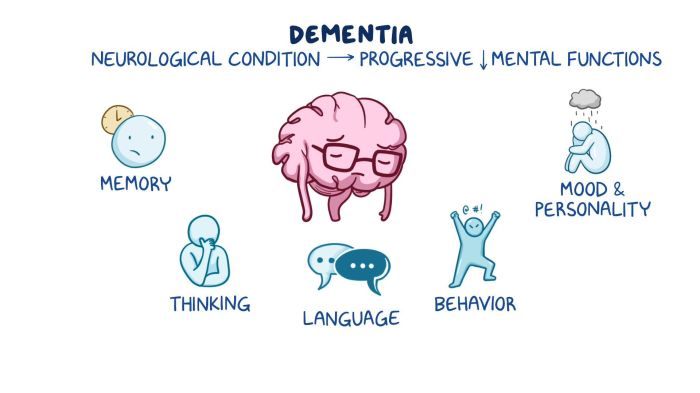
Cognitive impairment is widely recognized as the primary risk factor for wandering and elopement. Individuals with cognitive impairments, such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, may experience disorientation, confusion, and memory loss, which can lead to them becoming lost or wandering away from familiar surroundings.
Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment is a major risk factor for wandering and elopement, as it can affect a person’s ability to recognize familiar surroundings, understand instructions, and make sound decisions. This can lead to disorientation, confusion, and an increased likelihood of wandering or elopement.
Specific cognitive impairments that increase the risk of wandering and elopement include:
- Dementia
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Lewy body dementia
- Parkinson’s disease
- Huntington’s disease
Physical Limitations, What is the main risk factor for wandering and elopement
Physical limitations, such as mobility issues or sensory impairments, can also contribute to wandering and elopement. For example, a person with limited mobility may be unable to get around easily and may wander in search of assistance or a familiar place.
Sensory impairments, such as vision or hearing loss, can also increase the risk of wandering and elopement. A person with vision loss may be unable to see obstacles or recognize familiar landmarks, while a person with hearing loss may be unable to hear instructions or warnings.
Studies have shown that people with physical limitations are more likely to wander and elope than those without physical limitations. For example, one study found that people with dementia who had mobility problems were three times more likely to wander than those without mobility problems.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as unfamiliar surroundings or lack of supervision, can also increase the risk of wandering and elopement. For example, a person with dementia who is placed in a new environment may become disoriented and wander in search of a familiar place.
Lack of supervision is another environmental factor that can increase the risk of wandering and elopement. A person with dementia who is not supervised may be able to wander out of a home or care facility without being noticed.
Specific environmental hazards that should be addressed include:
- Unfamiliar surroundings
- Lack of supervision
- Poor lighting
- Cluttered or obstructed pathways
- Lack of safety features, such as alarms or door locks
Emotional Distress
Emotional distress, such as anxiety or depression, can also lead to wandering and elopement. For example, a person with anxiety may wander in search of a safe place or a familiar person.
Depression can also lead to wandering and elopement. A person with depression may wander in search of a place to be alone or to escape from their problems.
Emotional triggers that can lead to wandering and elopement include:
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Loneliness
- Boredom
Medications
Certain medications can also increase the risk of wandering and elopement. These medications include:
- Antipsychotics
- Sedatives
- Hypnotics
- Antidepressants
- Anticonvulsants
These medications can affect cognitive function and behavior, which can lead to wandering and elopement.
History of Wandering/Elopement
A person who has a history of wandering or elopement is at an increased risk for future events. This is because wandering and elopement are often a symptom of an underlying condition, such as dementia or Alzheimer’s disease.
Previous incidents of wandering or elopement should be considered when assessing the risk of future events. This information can help to develop a care plan that can help to prevent wandering and elopement.
FAQ Compilation: What Is The Main Risk Factor For Wandering And Elopement
What are the signs and symptoms of cognitive impairment?
Signs and symptoms of cognitive impairment may include memory loss, confusion, disorientation, difficulty with language and communication, and changes in behavior.
What are the different types of cognitive impairment?
There are many different types of cognitive impairment, including dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia.
What are the treatments for cognitive impairment?
There is no cure for cognitive impairment, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms. These treatments may include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes.