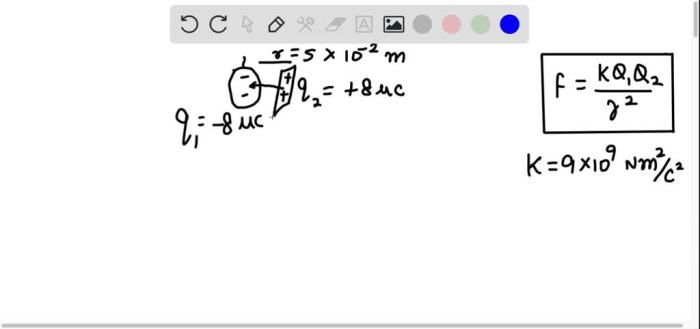
A balloon rubbed against denim gains electrostatic charge, a fascinating phenomenon that arises from the transfer of electrons between the two materials. This interaction, driven by friction, creates an imbalance of electrical charges, leading to a range of intriguing effects and practical applications.
When a balloon is rubbed against denim, electrons from the denim’s surface are transferred to the balloon’s surface. This transfer results in the balloon acquiring a net negative charge, while the denim gains a net positive charge. The charged balloon can then interact with other objects, demonstrating the effects of electrostatic charge.
Electrostatic Charge: A Balloon Rubbed Against Denim Gains

Electrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest. When a balloon is rubbed against denim, electrons are transferred from the denim to the balloon, creating a positive charge on the denim and a negative charge on the balloon. This separation of charges creates an electrostatic field around the balloon.
Other materials that can create an electrostatic charge when rubbed together include:
- Glass and silk
- Rubber and fur
- Plastic and wool
Friction plays a role in the generation of electrostatic charge by removing electrons from one material and transferring them to another.
Static Discharge
Static discharge occurs when a charged object comes into contact with a conductor. This causes the electrons to flow from the charged object to the conductor, neutralizing the charge. The sudden release of electrons can create a spark or a shock.
Conductors are materials that allow electrons to flow freely, while insulators are materials that do not allow electrons to flow easily. Metals are good conductors, while plastics and rubber are good insulators.
Examples of everyday situations where static discharge can be observed include:
- Touching a doorknob after walking across a carpet
- Getting out of a car and touching the metal frame
- Combing your hair on a dry day
Applications of Electrostatic Charge

Electrostatic charge has a wide range of practical applications, including:
- Electrostatic spray painting: Electrostatic charge is used to attract paint particles to the surface being painted, resulting in a more even and efficient coating.
- Air filters: Electrostatic charge is used to attract dust and other particles to the filter, improving air quality.
- Manufacturing of electronics: Electrostatic charge is used to hold small components in place during assembly.
- Textile manufacturing: Electrostatic charge is used to remove lint and other impurities from fabrics.
Many industries utilize electrostatic charge for specific purposes, such as the automotive industry, the electronics industry, and the textile industry.
Safety Considerations

Electrostatic charge can pose potential hazards, including:
- Electrostatic discharge: Electrostatic discharge can damage electronic components and cause fires.
- Dust explosions: Electrostatic charge can ignite dust particles, causing explosions in environments where there is a high concentration of dust.
Grounding and other safety measures are important to prevent electrostatic hazards. Grounding involves connecting a charged object to the earth, which allows the electrons to flow away and neutralize the charge. Other safety measures include using anti-static materials and avoiding working in environments with high levels of dust.
It is important to follow guidelines for handling charged objects and working in environments with electrostatic charge to ensure safety.
Questions Often Asked
What causes a balloon to gain a charge when rubbed against denim?
Friction between the balloon and denim transfers electrons from the denim to the balloon, resulting in the balloon gaining a negative charge and the denim gaining a positive charge.
What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator in terms of static electricity?
Conductors allow electric charges to flow freely through them, while insulators do not. In the context of a charged balloon, conductors allow the charge to dissipate quickly, while insulators retain the charge for a longer period.
What are some practical applications of electrostatic charge?
Electrostatic charge has various practical applications, including electrostatic spray painting, air filtration, and the manufacturing of electronics and textiles. In electrostatic spray painting, charged paint particles are attracted to the oppositely charged surface being painted, resulting in a more even and efficient coating.